“`html
When I explore the topic of illumination, one term frequently brightens the discourse: LED. So, what does LED signify? The led complete form is ‘Light Emitting Diode,’ a technology revolutionizing the way we light our environment. As a substitute for conventional lighting, LED provides energy-saving options that have dramatically altered lighting norms. Therefore, an led clarification extends beyond its technical meaning—it represents a shift toward sustainability and creativity in illumination.
Essential Insights:
- A Light Emitting Diode, or LED, emits light more effectively than standard bulbs.
- LEDs attain brightness via a method that generates less heat—a significant advantage for energy conservation.
- Grasping LEDs is crucial as they are central to low-energy and high-efficiency applications.
- The led complete form encapsulates the core of a technological revolution in lighting.
- Understanding what does led signify is merely the start of valuing its extensive influence.
Revealing LED: A Definition and Historical Background
As we investigate the domain of contemporary lighting, the term LED is one that frequently illuminates conversations about energy conservation and innovation. Thus, I am urged to inquire: What’s the narrative behind this groundbreaking technology?
The Significance of the Acronym LED
The LED abbreviation—commonly employed in both professional and informal discussions regarding lighting—denotes Light Emitting Diode. By definition, an LED is a semiconductor device that radiates light when an electrical current flows through it. The phrase ‘LED’ is not just another technical acronym; it embodies the essence of a technology that utilizes the power of electroluminescence in a compact and efficient format. Indeed, the led significance resonates with the notion of guiding us toward a more sustainable and technologically advanced future.
Historical Framework and The Development of LED Technology
The led origin narrative commences in the early 20th century with the revelation of electroluminescence. It’s intriguing to consider how the modest origins of this technology have emerged into the modern LED. Initially utilized as basic indicator lights, LEDs have undergone remarkable advancements, infiltrating nearly every facet of lighting. Presently, they brighten our vehicle headlights, backlight our gadget screens, and provide countless design options for general illumination. Technological progress has enabled LEDs to decrease in size while expanding their applications. The versatility they present has led to LEDs becoming a prevailing and preferred lighting choice across various sectors, underscoring the importance of comprehending the led abbreviation when discussing lighting solutions.
My journey into the realm of LEDs affirms that this technology is far more than an efficient source of light; it’s the harbinger of a luminous, energy-aware future. And with this, we embark on a new chapter, where LEDs continue to influence the radiant landscape of our existence in various manners.
Electrical Essence: How Do LEDs Create Light?
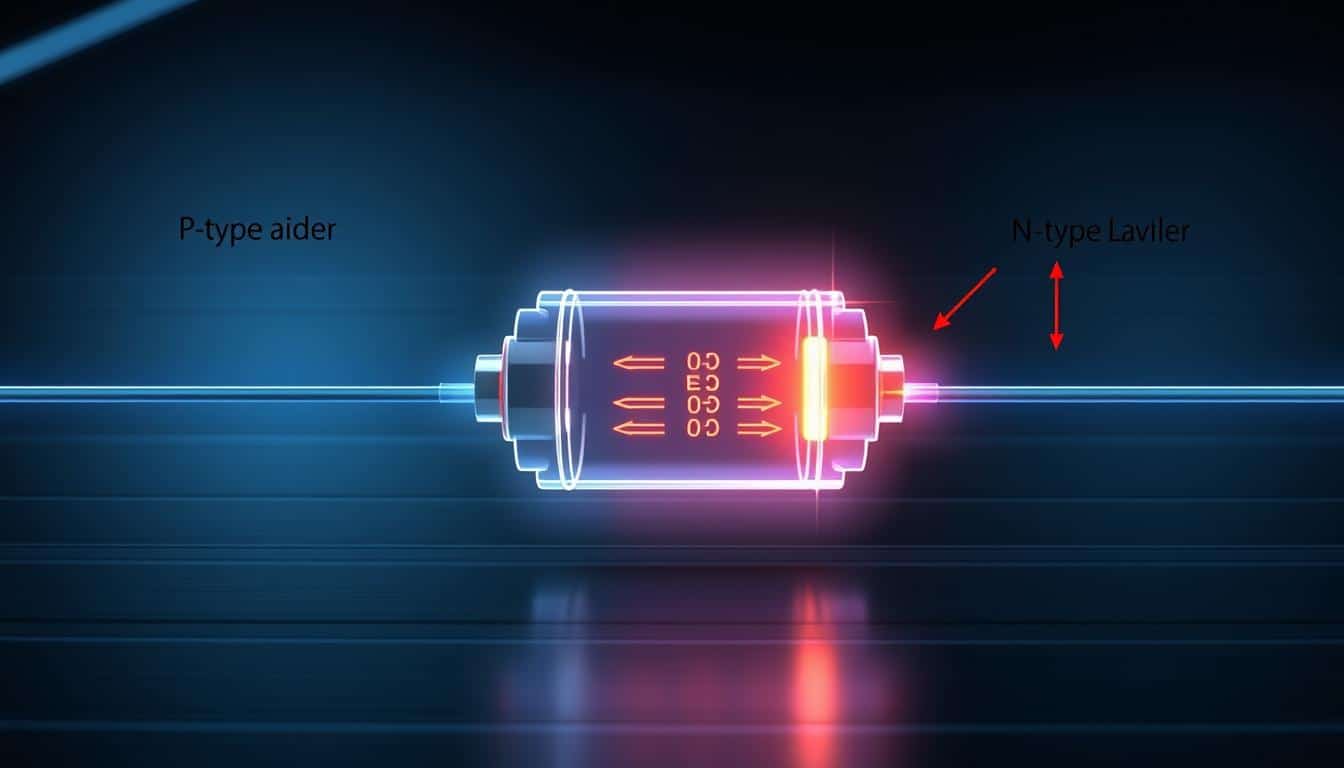
When embarking on a quest to unveil the led definition, it’s captivating to discover just how do LEDs function. These tiny power sources of illumination utilize electroluminescence—a method where light is generated as electrical current traverses a semiconductor material contained within the diode. This substance is crucial, as it is responsible for the emission of photons that converge into the visible spectrum, generating light that’s brilliant and energy-efficient.
In contrast to the omni-directional light emission of incandescent bulbs that scatter light and heat in every direction, LEDs are renowned for their focused light output. This targeted strategy to illumination necessitates innovative engineering to ensure their use in everyday settings like room lighting and street lamps. The precision of LEDs, directing light exactly where it is needed, highlights their operational excellence.
LED technology signifies a new era in illumination, where efficiency is synonymous with brilliance. The led lights that we recognize today exemplify the perfect harmony between advanced engineering and the core principles of physics.
| Feature | Incandescent Bulb | LED |
|---|---|---|
| Light Emission | Heat and light in all directions | Directional light output |
| Energy Effectiveness | Less effective; Higher heat output | Up to 90% more efficient than incandescent |
| Heat Management | No designated mechanism | Heat sinks absorb and disperse heat |
| Design Application | Limited by glass bulb restrictions | Flexible; Facilitates innovative design potentials |
| Lifespan | Shorter due to filament wear | Longer with minimal lumen depreciation over time |
| Cost Efficiency | Less economical over time | High initial cost but generates savings in the long term |
As I observe the LED in action, it’s easy to acknowledge its transformative influence. It has indeed redefined the very nature of how we utilize light in our lives, from the gentle glow of a reading lamp to the bright safety of street lights. Its functionality, combined with its environmental impact, illustrates an innovative future rooted in sustainability, fortified by this outstanding technology.
The Lifecycle of LEDs: Understanding Durability and Longevity
As I delve into the sphere of sustainable lighting, it’s hard not to be impressed by the resilience and enduring quality that characterize LED technology. Recognized for their remarkable led longevity, these luminous wonders offer an enlightening perspective on energy-efficient illumination. Join me as we shine a light on the importance of led durability and the phenomenon known as lumen depreciation.
Exploring ‘Lumen Depreciation’: What It Indicates for LED Life Span
The concept of lumen depreciation is pivotal to comprehending the longevity of an LED. It’s not about the abrupt burnout more prevalent in incandescent bulbs, but rather a gradual and steady decline in brightness. Specifically, led longevity is assessed by the point at which the output diminishes to 70% of its initial brilliance. This characteristic of led durability is crucial to why they are often praised for their exceptional lifespan, combined with efficiency.
Contrasting LED Lifespan with Traditional Light Sources
The distinction between LED and traditional light sources is striking and enlightening. While the tungsten filaments of incandescent bulbs succumb to time, the luminosity of LEDs endures. They radiate light for an astounding duration, logging hours that surpass those of their incandescent and compact fluorescent rivals. It’s essential to emphasize that the prolonged life of LEDs not only shines in longevity but also in diminished energy consumption and maintenance expenses.
| Light Source | Lifespan (hours) | Lumen Depreciation | Energy Efficiency | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Incandescent Bulb | 1,000 | Rapid due to filament deterioration | Low | |
| Compact | Fluorescent (CFL) | 8,000 to 10,000 | Moderate over time | Medium |
| LED | 25,000 to 50,000 | Gradual; based on 30% reduction | High |
My examination into the lifespan of LEDs reveals a capability that surpasses mere luminosity. With impressive LED longevity and minimal lumen loss, LED technology shines as an emblem of sustainability—illuminating a hopeful path for the future of global lighting.
Exploring LED Uses in Everyday Life
As I navigate through different environments and moments, I can’t help but recognize how LED implementations have effortlessly woven themselves into my daily experiences. From the instant I turn on my bedroom light to the period I shut down my mobile device, LEDs are a steadfast presence, bathing my tasks in their energy-efficient illumination.

At home, LEDs have assumed a prominent role in where to use led bulbs—from the ambient luminosity in my living room to the focused lighting above my kitchen area. Yet their usefulness extends beyond home environments. In my vehicle, LED headlights navigate the darkness with accuracy, and inside, dashboard indicators depend on LEDs for optimal clarity.
Even as I type, the gentle backlighting of my laptop’s keyboard stems from LEDs, allowing me to work at ease without eye strain. Furthermore, in my leisure activities, when I care for my indoor plants, LED grow lights supply the essential light spectrums my greenery requires for photosynthesis. The adaptability of LED technology to fulfill specific needs demonstrates its versatility and efficiency.
Below is a table that encapsulates the scope of LED implementations that brighten our daily routines:
| Application | Location | Function | Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Home Lighting | Bedrooms, Kitchens, Living Rooms | Ambiance and Task Lighting | Energy Efficiency and Longevity |
| Automotive Lighting | Headlights, Dashboard Displays | Visibility and Safety | Durability and Performance |
| Mobile Devices | Smartphones, Tablets, Laptops | Displays and Indicators | Low Power Consumption |
| Specialized Industries | Horticulture, Medicine, Art | Grow Lights, Surgical Lights, Display Lighting | Customized Lighting Solutions |
Indeed, the influence of LEDs in our lives is as varied as it is crucial. The emergence of LED implementations across different sectors illustrates how suitable and vital this technology has become. It’s evident that the inquiry isn’t where to use led bulbs anymore—it’s actually where don’t we use them.
The Technical Aspects of LED Lighting Efficiency
In my investigation of advancements in lighting technology, the theme of LED lighting efficiency presents a captivating story. LEDs have secured their place in the lighting sector, primarily due to two significant qualities—efficiency and energy management.
What Differentiates LEDs in Terms of Energy Use?
The notable disparity in led energy usage compared to conventional lighting alternatives is truly remarkable. Much of the dialogue surrounding sustainable energy practices in lighting invariably emphasizes LEDs as representatives of efficiency. In essence, LEDs can produce light up to 90% more effectively than their incandescent equivalents—a reality that underscores why this technology is rapidly becoming common. This goes beyond merely saving on utility expenses; it’s about a dedicated movement towards eco-friendly living.
Why LEDs Are Viewed as Directional Light Sources
Another characteristic that elevates LEDs above traditional lighting technologies is their natural directional light output. In contrast to the diffused approach of incandescent and compact fluorescent lighting (CFL), LEDs direct light in a focused manner. This attribute not only reduces waste but also enhances the practical use of lighting where it’s most needed. Whether highlighting a piece of artwork or illuminating a walkway, the directional quality of LED lighting serves a purpose and promotes efficiency.
To illustrate the differences in energy consumption and efficiency between LED and traditional lighting technologies, consider the following comparative data:
| Light Source | Energy Efficiency | Directionality | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Incandescent Bulb | Least efficient | Omni-directional | General-purpose |
| Compact Fluorescent (CFL) | Moderately efficient | Omni-directional | General-purpose |
| LED | Most efficient | Directional | Task-specific to general-purpose |
The compilation of my reflections on the efficiency of LED lighting fosters a deeper appreciation for how this technology not only brightens our environments but also champions energy conservation and the judicious use of our valuable resources.
LEDs and Their Interaction with Heat
In exploring the domain of LED technology, I’ve discovered that one of the key characteristics of LEDs is their ability to illuminate spaces without generating excessive heat. However, effectively managing the heat they do produce is vital for ensuring their lifespan and efficiency. Let’s investigate further how heat sinks are instrumental and which thermal management techniques are necessary for optimizing LEDs.
The Importance of Heat Sinks in LED Functionality
My interest in the efficient operation of LEDs extends beyond their light-producing capabilities; it also encompasses the clever methods they employ to manage the unavoidable by-product: heat. Although being cooler and more energy-efficient than traditional bulbs, LEDs still emit heat that must be properly managed. The inclusion of heat sinks in LED products is not just a design consideration, but a critical necessity. These components absorb the heat generated by the LED and disperse it into the surrounding area. This effective thermal regulation is what prevents LEDs from overheating, thereby ensuring they perform optimally for an extended duration.
Thermal Management Techniques for Extending LED Lifespan
To truly value the innovation in LED lighting systems, one must examine their thermal management methods which are crucial for maintaining steady light output over the long term. Different LED products feature unique heat sink configurations that accommodate their specific shapes, from those aligning with traditional bulb forms to those incorporated into complex lighting designs. I have personally seen how each of these designs reflects the ingenuity present in the realm of LED thermal management.
“Thermal management is the single most important factor in the successful performance of an LED.” – Department of Energy
Here’s an informative table showcasing various heat sink designs and their contributions to managing LEDs and heat:
| Heat Sink Design | Material | Thermal Conductivity | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pin Fin | Aluminum | Elevated | Improves airflow, expands surface area |
| Plate Fin | Copper | Extremely High | Efficient at reduced airflow, durable |
| Passive | Graphite | Moderate | Employs natural convection |
| Active | Composite | Flexible | Integrates a fan or pump for heat distribution |
When I reflect on the assortment of heat sinks utilized in the pursuit of optimal LED thermal management, it reminds me of the meticulous design that goes into each LED product we utilize. It fosters a greater appreciation for the innovative spirit propelling the LED sector forward, transforming the challenges posed by LEDs and heat into avenues for progress.
Color Dynamics of LED Lights
As I enhance my comprehension of LED technology, I’m fascinated by the complex pathways through which LEDs can generate a broad spectrum of colors, including the desired white light LED. This ability to produce a varied selection of led color options is not merely a feature but a revolutionary asset for many applications.
The Physics of Generating White Light with LEDs
In the production of white light, LEDs utilize ingenious methods. Some combine red, green, and blue LEDs, which mix to emit white light, while others are enveloped in a phosphor coating that, when stimulated by blue or ultraviolet light from the LED, emits a white glow. This phosphor conversion is strikingly efficient, producing white light LEDs that have become common in households and industries due to their versatility and effectiveness.
This adaptation of LEDs not only broadens our color range but also amplifies the utility of lighting, facilitating various uses from task-oriented to mood-enhancing environments. At the heart of white light LED technology is a profound interaction between physics and design innovation, which I find truly captivating.
Investigating the Extensive Range of LED Color Options
The led color options available today are vast, permitting customization like never before. LEDs provide a distinct choice of colors determined by the specific wavelength of emitted light, quantified in nanometers for color LEDs. From deep blues to vivid reds, the application of LED color options is extensive, catering to specialized requirements such as plant development in horticulture, where specific wavelengths have demonstrated advantages in photosynthesis, and aesthetic displays that necessitate a particular ambiance.
White LEDs also possess a color temperature, measured in Kelvin, which spans from the warm white of a sunset at 2700K to the bright midday sun at 6500K. This adaptability is what renders LED technology so enticing, offering tailored solutions whether I’m reading under a warm white bulb or working in an office illuminated by cool, daylight white light.
The exploration of LEDs and their color dynamics uncovers a blend of art and science—a partnership that continues to transform our visual and functional landscape. It’s not solely about illuminating a room; it’s about creating an experience. The variety of LED color options achieves precisely this, crafting possibilities confined only by imagination.
What Does LED Stand For?
As an inquisitive adventurer in the continually evolving realm of technology and sustainability, I’ve frequently contemplated the significance behind the acronym LED. The led full form, Light Emitting Diode, embodies a vast world of innovation within its brief letters. This compact yet potent semiconductor device has altered the course of illumination, serving as a beacon for the environmentally aware and efficiency-focused society.
My grasp of what does led mean extends beyond the basic mechanics of light creation; it signifies a transformation in design philosophy and function, paving the way for environmentally friendly and cost-effective lighting solutions. LEDs exemplify a greener approach to lighting, one that conserves our planet’s resources while delivering outstanding performance that far exceeds traditional lighting technologies in both energy efficiency and durability.
With my expanding curiosity, I explored the design of the LED, admiring how it operates with remarkable simplicity and effectiveness. An LED illuminates our spaces by allowing electricity to flow through its microchip, a process that then lights up the small sources of light known as LEDs. This mechanism produces visible light—and does so with a finesse that conserves energy and ensures a prolonged operational lifespan. The wonder of LED technology doesn’t cease at individual diodes; it extends into the intricate networks of LED lighting that illuminate our cities and homes.
Reflecting on the fundamental question, what does led mean, I am prompted to argue that it represents more than simply Light Emitting Diode. It symbolizes a conscious choice for sustainability, a partner in energy conservation, and an investment in our collective future. The led full form is not just an abbreviation; it’s a representation of innovation and the continuous movement towards a brighter, cleaner world.
Powering LEDs Securely for Optimal Brightness and Efficiency
Diving into the specifics of LED illumination, I’ve uncovered that achieving the ideal balance between brightness and efficiency revolves around the LED’s drive current. This current, quantifiable in both milliamps (mA) and amps (A), dictates the amount of light an LED will emit. Grasping the subtleties of powering LEDs is crucial to ensure that light output is maximized without jeopardizing the diode’s lifespan. Now, let’s take a closer look at the effects of drive current and explore the guidelines for properly configuring an LED power supply.
Comprehending Drive Current and Its Effects on LED Brightness
When I first experimented with LEDs, it became immediately clear that drive current is not just a figure to be acknowledged, but a critical component in the luminous equation. Surpassing the rated drive current can significantly shorten the lifespan of an LED, while providing too little can lead to a dim, disappointing performance. It’s a complex interplay of electrical input and light output that can only be performed by following the specifications laid out by manufacturers.
Recommendations for Proper LED Power Supply Configuration
The task of configuring the ideal LED power supply commences with a precise comprehension of the LED’s needs—this includes the forward voltage and the maximum rated drive current. Adhering to these specifications is vital not only to protect the LED but also to attain peak luminosity efficiently. Below, I’ve assembled a table that highlights the factors to ponder when powering LEDs, offering insights into the delicate balance of electrical components and their coordinated operation.
| Factor | Description | Effect on LED Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Drive Current | The electric current provided to the LED. | Directly affects brightness; excessive current can diminish lifespan. |
| Forward Voltage | The voltage at which the LED permits current to flow through. | Essential for ensuring LEDs illuminate; must align with power supply voltage. |
| Power Supply Category | Constant current versus constant voltage supplies for LEDs. | Should align with LED specifications to avert overload. |
| Heat Management | Thermal dissipation elements such as heat sinks. | Prevents overheating, sustaining brightness and prolonging lifespan. |
| Dimming Functionality | Power supplies facilitating variable light output. | Permits supervision over brightness while regulating energy usage. |
| Wiring and Installation | Proper configuration of the circuit and LEDs. | Averts failures and enhances power distribution to LEDs. |
The expertise in power supply arrangement transcends mere mathematical accuracy. It’s about orchestrating a harmony of electrical components that operate in concert to produce the most radiant and sustainable LED illumination. As I persist in powering LEDs in my projects, I regularly remind myself of the significance of these principles to secure the durability and vibrant operation of each diode.
Acknowledging the Significance of ENERGY STAR Ratings for LEDs
In my pursuit to highlight the importance of energy efficiency and quality assurance in illumination, the ENERGY STAR certification rises as a crucial benchmark. This rating is more than a mere tag; it’s a declaration of the performance and dependability that consumers can anticipate from energy star certified led lighting. I discover that exploring the nuances of what qualifies an LED product for this prestigious certification yields a deeper understanding of the commitment to quality led products within the industry.
Interpreting ENERGY STAR Certification Criteria
My investigation into LED lighting certifications has deepened my knowledge of the ENERGY STAR program. This certification is not easily granted; it is bestowed upon LED products that satisfy exacting standards across various performance metrics. These standards guarantee that any energy star certified led lighting not only provides exceptional color quality and light output but also showcases outstanding light distribution. In order to achieve this sought-after endorsement, every LED bulb is subjected to rigorous testing to confirm its conformity with strict performance and labeling regulations.
The certification standards also encompass long-term testing, acting as a compelling assurance of the LED’s longevity. Furthermore, manufacturers’ commitment to consumer confidence is reflected in the mandated minimum three-year warranty for ENERGY STAR certified products. This combination of thorough evaluation, verified adherence, and a robust warranty emphasizes the superiority and trustworthiness that ENERGY STAR certified LEDs deliver.
Ensuring Quality and Performance of LED Products
What captivates me the most regarding ENERGY STAR rated LED products is the reassurance they provide to consumers. When I opt for an ENERGY STAR certified LED, I am confident in selecting a quality led product that will not falter in performance over time. Whether it’s the durability, consistency of light output, or the strength of the product under various environmental conditions, these certified products distinguish themselves in the market, offering both energy savings and a significant contribution towards environmental responsibility.
| Energy Efficiency Standards | Importance for Consumers |
|---|---|
| Strict Color Quality Standards | Guarantees natural and uniform lighting in your surroundings |
| Exacting Light Output and Distribution Standards | Provides adequate and focused illumination for diverse needs |
| Comprehensive Warranty Protection | Ensures product reliability and manufacturer assistance |
| Verified Performance and Label Compliance | Assures that products function as advertised |
| Energy Savings | Lowers electricity costs and reduces environmental footprint |
Indeed, ENERGY STAR certification symbolizes a symbol of trust and quality within the realm of LED lighting. As I incorporate these LEDs into my environment, I do so with the knowledge they are supported by rigorous standards that not only brighten my immediate space—but also hold promise for our planet’s future.

Conclusion
As I ponder the journey through the innovative realm of LED technology, I am reminded of the significant progression and the noteworthy advances made by this revolutionary lighting solution. From its beginnings as a simple indicator light to its rise as a prominent source in eco-friendly design and technology, the advantages of LEDs have illuminated pathways widespread. The led significance in our everyday lives is undeniable; it signifies a commitment to development that balances exceptional performance with minimal environmental repercussions.
The advantages of LEDs resonate significantly with those of us mindful of the necessity for energy conservation. With unmatched energy efficiency, remarkable longevity, and a variety of uses that blend aesthetics with practicality, LED technology stands as a testament to human creativity. Each advancement—from the development of phosphor-based white LEDs to the evolution of smart, interconnected lighting systems—has paved the way for a luminous, sustainable tomorrow.
My exploration of LEDs culminates in the realization that this technology is more than a wise selection for illumination—it is a bold declaration in favor of a greener planet. It is this crucial role of LEDs in advocating for sustainability, enhancing our quality of life, and transforming the industry that solidifies their place as a beacon of innovation. Truly, the led benefits we reap today are merely indicators of the potential that lies ahead in our radiant journey forward.
FAQ
What does LED denote?
LED stands for Light Emitting Diode.
Can you briefly explain LED?
An LED is a semiconductor light source that emits illumination when an electric current passes through it. It’s renowned for its energy efficiency and durability.
What is the origin of LED technology?
LED technology has its roots in the early discovery of electroluminescence during the 20th century and has progressed into the effective light sources utilized widely today.
How do LEDs generate light?
LEDs create light via a process called electroluminescence, where an electrical current flows through a semiconductor material, releasing photons that we perceive as light.
What is lumen depreciation in LED lighting?
Lumen depreciation pertains to the gradual decrease in brightness of an LED over time, which serves as an indicator of its lifespan rather than an abrupt failure.
How does the lifespan of LEDs measure up against traditional light sources?
LEDs offer a significantly longer lifespan compared to conventional incandescent and compact fluorescent bulbs, frequently lasting tens of thousands of hours before reaching their end of life.
“““html
lumen reduction.












Emersyn
LEDs are overrated! Incandescent bulbs forever! Whos with me? 🔥💡