Have you ever wondered what makes LED lights shine so brightly while using so little energy? Understanding how LED lights work can help you make smarter choices for your home and save on electricity bills.
You’ll discover the simple, step-by-step process behind LED lighting. By the end, you’ll see why LED lights are not just bright but also incredibly efficient and long-lasting. Keep reading, and you’ll never look at a light bulb the same way again!
Basics Of Led Technology
LED technology is part of many devices around us. It uses tiny lights that save energy and last long. Understanding how LEDs work helps us see why they are so popular. The basics of LED technology explain how light is made and what parts are inside.
What Is An Led
An LED is a small light source. It stands for Light Emitting Diode. Unlike old bulbs, it does not have a filament. LEDs are solid and very durable. They use less power and produce less heat.
How Leds Emit Light
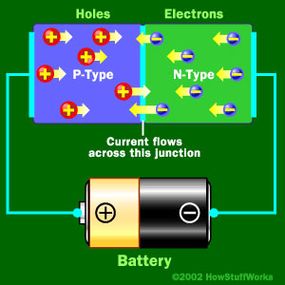
LEDs create light using electricity and materials. When electric current passes through, electrons move inside. These electrons meet holes in the material. This meeting releases energy in the form of light. This process is called electroluminescence.
Key Components Of An Led
An LED has a few main parts. The chip is the tiny piece that makes light. It sits between two layers of semiconductor material. The anode and cathode connect the LED to power. A lens covers the chip to focus light. These parts work together to create bright, efficient light.
How Electricity Powers Leds
Electricity is the key to making LED lights shine. It flows through the LED and causes light to appear. This process is simple but amazing. Understanding how electricity powers LEDs helps us appreciate these small lights.
Here is how it works step by step. Each part of the LED plays a role in turning electric energy into light. Let’s break down the process.
Role Of Electric Current
Electric current is the flow of tiny particles called electrons. These electrons move through the LED’s circuit. When the current reaches the LED, it provides energy to the device. This energy is what starts the light-making process.
The current must flow in the right direction. If it flows backward, the LED will not light up. Proper current flow is essential for the LED to work well and last long.
Semiconductor Materials In Leds
LEDs use special materials called semiconductors. These materials control the flow of electric current. Semiconductors have two layers: one with extra electrons and one with fewer electrons.
The two layers create a boundary called a junction. This junction is where the magic happens. It lets electrons move across and release energy in the form of light.
Electron Movement And Light Generation
When electricity flows, electrons move from one layer to another. They jump across the junction inside the LED. As they jump, they lose energy.
This lost energy turns into light. The color of the light depends on the semiconductor material used. This simple electron movement creates the bright light we see from LEDs.
Step-by-step Led Operation
Understanding how LED lights work involves breaking down the process into clear steps. Each step explains how electricity turns into light inside the LED. This simple guide helps you see how LEDs shine bright and save energy.
Follow these steps to learn the basic operation of LEDs. This knowledge makes it easier to appreciate the technology behind everyday lighting.
Applying Voltage
LEDs need electricity to work. When voltage is applied, current starts to flow through the LED. This flow moves electrons from one side of the LED to the other. The voltage pushes the electrons into the LED’s active area. This step is the first spark for light production.
Electron-hole Recombination
Inside the LED, electrons meet holes. Holes are places where electrons are missing. When electrons fill these holes, they lose energy. This loss is important because it creates the light. This process is called recombination. It happens in the LED’s special layer made for light emission.
Photon Emission Process
Energy lost during recombination turns into photons. Photons are tiny particles of light. These photons escape the LED and produce visible light. The color of the light depends on the LED material. This final step gives us the bright light we see from LEDs.

Factors Affecting Led Performance
LED lights are popular for many reasons. Their performance depends on several key factors. These factors influence how bright, efficient, and long-lasting the LEDs are. Understanding them helps in choosing the right LED light for your needs.
Heat Management
LEDs produce less heat than traditional bulbs but still generate some heat. Excess heat can damage the LED and reduce its lifespan. Proper heat sinks and cooling designs help remove heat. This keeps the LED cool and working well for longer.
Color And Brightness Control
LEDs can emit different colors by mixing light from various diodes. The color quality depends on the materials used inside the LED. Brightness is controlled by adjusting the electric current. Careful control ensures the light is clear and consistent.
Energy Efficiency
LEDs use less electricity than other lights. Their design turns most energy into light, not heat. This saves power and lowers electricity bills. Higher efficiency means the LED can run longer on less energy.
Different Types Of Led Lights
LED lights come in various types, each designed for different uses. Understanding these types helps you choose the right light for your needs. Different LEDs offer different brightness, size, and power efficiency. Here are the most common types of LED lights.
Standard Leds
Standard LEDs are small and use low power. They are common in indicator lights, screens, and small devices. These LEDs are energy-efficient and last a long time. They produce light in many colors, including red, green, and blue. Standard LEDs are affordable and easy to use.
High-power Leds
High-power LEDs provide much brighter light than standard ones. They are used in flashlights, car headlights, and street lights. These LEDs need special cooling systems to prevent overheating. High-power LEDs use more energy but offer strong, focused light. They last longer than traditional bulbs.
Oleds And Future Innovations
OLEDs, or organic LEDs, use organic materials to create light. They are thin, flexible, and can be made into screens or lights. OLEDs provide bright, clear light with low power use. Future LED types may include smarter, more efficient designs. These advances aim to improve brightness and reduce energy use even more.
Common Applications Of Leds
LED lights have many uses across different areas. Their efficiency and long life make them popular. People choose LEDs for various lighting needs. Below are some common applications of LED lights.
Residential Lighting
LEDs brighten homes with less energy. They work well in lamps, ceiling lights, and night lights. Their low heat helps keep rooms cool. Many use LEDs for kitchen and bathroom lighting. These lights offer clear, bright light for daily tasks.
Commercial And Industrial Uses
Businesses use LED lights to save money. Offices, stores, and factories rely on LED lighting. LEDs last longer than traditional bulbs. This reduces maintenance and replacement costs. Bright LEDs improve worker safety and product visibility.
Specialized Lighting Solutions
LEDs fit special needs like street lights and car headlights. They also appear in signs and traffic signals. Medical devices use LEDs for precise lighting. Their small size allows use in tight spaces. LEDs provide bright, focused light for many tasks.

Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Led Lights Produce Light?
LEDs produce light through electroluminescence. When electric current passes through a semiconductor, it emits photons, creating visible light efficiently.
What Components Are Inside An Led Light?
An LED contains a semiconductor chip, electrodes, and a lens. The semiconductor emits light, while the lens directs and protects it.
Why Are Led Lights More Energy Efficient?
LEDs use less power because they convert most energy into light, not heat. This efficiency reduces electricity consumption significantly.
How Long Do Led Lights Typically Last?
LEDs last between 25,000 to 50,000 hours. Their long lifespan reduces replacement frequency and maintenance costs.
Conclusion
LED lights work by passing electricity through tiny chips. These chips emit light when powered. The process uses less energy than traditional bulbs. LED lights last longer and stay cooler. They come in many shapes and colors. Understanding their function helps you choose the right light.
Small steps create bright, efficient lighting solutions. Now you can see how LEDs bring light to life. Simple science, great results.










Leave a Reply