Is your LED light not working, leaving you in the dark and wondering what went wrong? You rely on these lights every day for clear, bright illumination, so when they fail, it can be frustrating and confusing.
But don’t worry—understanding why your LED light doesn’t work is easier than you think. You’ll discover simple, effective ways to fix the problem quickly. Keep reading, and you’ll soon have your space shining bright again.

Common Causes Of Led Failure
LED lights are popular for their brightness and energy efficiency. Yet, they sometimes stop working unexpectedly. Understanding why LEDs fail helps fix problems quickly and avoid future issues.
Several common causes lead to LED failure. These causes often involve electrical or environmental factors. Identifying the root cause makes repair easier and saves time.
Power Supply Issues
LEDs need a steady power supply to work correctly. Fluctuations or low voltage can cause the light to flicker or stop. Using the wrong power supply or a damaged adapter can also harm the LED.
Faulty Wiring
Poor wiring connections often cause LED failure. Loose or broken wires interrupt the flow of electricity. Incorrect wiring during installation can cause short circuits or no power to the LED.
Driver Problems
The driver controls the LED’s power and current. A failing or incompatible driver leads to flickering or complete shutdown. Some LEDs need specific drivers, so using the wrong type causes damage.
Overheating Effects
Heat can shorten an LED’s lifespan significantly. Poor ventilation or excessive current creates high temperatures. Overheating causes the LED to dim, flicker, or fail entirely.

Basic Troubleshooting Steps
When an LED light does not work, basic troubleshooting helps find the problem fast. These steps guide you through simple checks. They can save time and avoid unnecessary costs.
Start by checking the power source. Then look closely at the bulb and socket. Testing with a different LED is a quick way to spot a faulty bulb. Finally, reset the circuit to clear any electrical issues.
Check The Power Source
Make sure the power switch is on. Verify the outlet or power strip has electricity. Use a different device to confirm the outlet works well. Check for any tripped circuit breakers or blown fuses. No power means the LED won’t light up.
Inspect The Bulb And Socket
Turn off the power before handling the bulb. Look for visible damage on the LED bulb. Check if the bulb is securely screwed into the socket. Clean any dirt or corrosion from the socket. A loose or dirty connection can stop the light from working.
Test With A Different Led
Replace the non-working LED with another one that is known to work. This test shows if the original bulb is defective. If the new LED lights up, the old bulb needs replacement. If not, the problem lies elsewhere in the circuit.
Reset The Circuit
Turn off the power supply to the LED light. Wait a few seconds before turning it back on. This resets the electrical circuit and can fix minor glitches. Check if the LED lights up after the reset. Sometimes, a simple reset solves the issue.
Fixing Wiring And Connection Problems
Fixing wiring and connection problems can bring your LED light back to life. Loose wires or poor contacts often stop the light from working. Checking and fixing these parts can solve the issue quickly.
Tighten Loose Connections
Loose connections cause power loss and flickering. Turn off the power before touching wires. Use a screwdriver to tighten any loose screws. Make sure wires are firmly attached to terminals. A secure connection improves electrical flow and light performance.
Replace Damaged Wires
Wires can break or wear out over time. Look for cracks, cuts, or burnt spots on wires. Replace any damaged wire with new ones of the same size. Use wire strippers to remove insulation carefully. Connect new wires tightly to avoid future problems.
Secure The Socket Properly
The socket holds the LED bulb in place. A loose or broken socket can stop the light from working. Check if the socket fits the bulb snugly. Tighten screws or clips that hold the socket. Replace the socket if it is cracked or damaged.
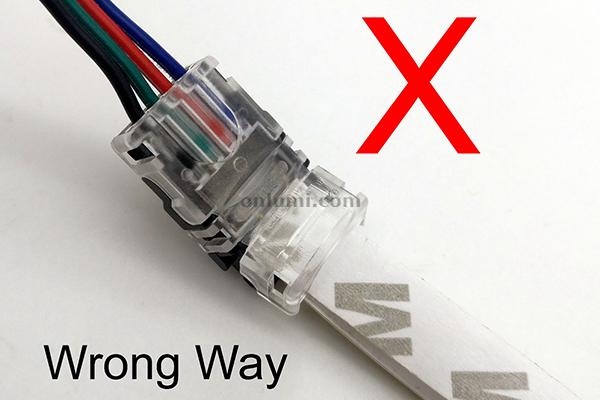

Dealing With Driver And Transformer Issues
LED lights rely on drivers and transformers to work correctly. These parts control the power that reaches the LED. Problems with drivers or transformers often cause LED lights to stop working. Understanding how to deal with these issues helps fix the problem fast.
Identify Driver Malfunctions
Check if the LED driver is making any noise or smells burnt. A driver that is too hot or flickers can be faulty. Use a multimeter to test the voltage output. If the voltage is low or unstable, the driver is likely bad.
Swap Out Faulty Drivers
Turn off the power before removing the driver. Replace it with one that matches the LED’s power needs. Test the light after installation to ensure it works. Swapping a bad driver often fixes the problem quickly.
Use Compatible Transformers
Match the transformer’s voltage and wattage to the LED’s specifications. Using the wrong transformer can cause flickering or no light at all. Check the transformer’s label for compatibility details. Proper transformers keep LED lights stable and bright.
Preventing Future Led Failures
Preventing future LED failures helps save money and time. Proper care extends the life of your LED lights. Small steps make a big difference in performance and durability.
Focus on key areas like power management, heat control, and component quality. These factors keep LEDs working longer and avoid common problems.
Avoid Overloading Circuits
Overloading circuits causes LEDs to burn out quickly. Check the power limits of your circuit before adding new lights. Spread the load evenly to reduce stress on components. Use circuit breakers or fuses to protect your system. Safe power use prevents sudden LED failures and hazards.
Ensure Proper Ventilation
Heat damages LED chips and drivers. Keep LED fixtures in well-ventilated areas to cool them naturally. Avoid enclosing lights in tight spaces without airflow. Use fans or vents if needed for extra cooling. Proper ventilation lowers temperature and boosts LED lifespan.
Use Quality Components
Cheap parts often cause LED problems and early failure. Choose LED bulbs, drivers, and wiring from trusted brands. High-quality components work better and last longer. Invest in good materials to avoid frequent replacements. Quality parts improve overall lighting safety and efficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why Is My Led Light Not Turning On?
Your LED light may not turn on due to a faulty power source, loose connections, or a burned-out bulb. Check the power supply and wiring first. Replace the LED if needed. Sometimes, a faulty switch or driver can also cause issues.
How To Fix An Led Light Flickering Issue?
Flickering LED lights often indicate a loose connection, incompatible dimmer switch, or voltage fluctuations. Tighten all wiring connections and use LED-compatible dimmers. If flickering persists, check the LED driver or replace the bulb to resolve the issue.
Can A Faulty Led Driver Cause Light Failure?
Yes, a faulty LED driver can cause LED lights not to work. The driver regulates power to the LED. If it malfunctions, the LED may fail to light up. Replacing the driver usually fixes this problem efficiently.
What Causes An Led Light To Suddenly Stop Working?
LED lights can stop working due to power surges, overheating, or internal component failure. Check for overheating signs and ensure proper ventilation. If the LED is damaged, replacement is often the only solution.
Conclusion
LED lights not working can feel frustrating. Check the power source first. Make sure the bulb fits correctly. Test the light in another socket. Sometimes, the LED itself may be faulty. Replacing the bulb often solves the issue. Don’t ignore wiring problems—they can cause failure too.
Simple steps help you fix most LED light problems. Keep these tips handy for quick troubleshooting. Bright lighting is just a few checks away. Stay patient and try these easy fixes.










Leave a Reply